A security vulnerability in the GNU Bourne Again Shell (Bash), the command-line shell used in many Linux and Unix operating systems, could leave systems running those operating systems open to exploitation by specially crafted attacks.
The bug, discovered by Stephane Schazelas, is related to how Bash processes environmental variables passed by the operating system or by a program calling a Bash-based script. If Bash has been configured as the default system shell, it can be used by network–based attackers against servers and other Unix and Linux devices via Web requests, secure shell, telnet sessions, or other programs that use Bash to execute scripts.
Because of its wide distribution, the vulnerability could be critical, though it may not be nearly as dangerous. The vulnerability affects versions 1.14 through 4.3 of GNU Bash. Patches have been issued by many of the major Linux distribution vendors for affected versions, including:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (versions 4 through 7) and the Fedora distribution
- CentOS (versions 5 through 7)
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS, 12.04 LTS, and 14.04 LTS
- Debian
A test on Mac OS X 10.9.4 (“Mavericks”) by Ars showed that it also has a vulnerable version of Bash. Apple has not yet patched Bash, though it just issued an update to “command line tools.”
While Bash is often thought of just as a local shell, it is also frequently used by Apache servers to execute CGI scripts for dynamic content (through mod_cgi and mod_cgid). A crafted web request targeting a vulnerable CGI application could launch code on the server. Similar attacks are possible via OpenSSH, which could allow even restricted secure shell sessions to bypass controls and execute code on the server. And a malicious DHCP server set up on a network or running as part of an “evil” wireless access point could execute code on some Linux systems using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol client (dhclient) when they connect.
There are other services that run on Linux and Unix systems, such as the CUPS printing system, that are similarly dependent on Bash that could be vulnerable.
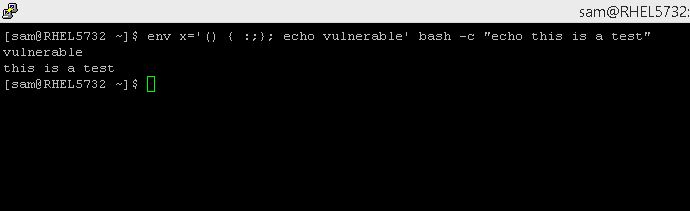
There is an easy test to determine if a Linux or Unix system is vulnerable. To check your system, from a command line, type:
env x='() { :;}; echo vulnerable' bash -c "echo this is a test"
If the system is vulnerable, the output will be:
vulnerable
this is a test
An unaffected (or patched) system will output:
bash: warning: x: ignoring function definition attempt
bash: error importing function definition for `x'
this is a test
The fix is an update to a patched version of the Bash shell. To be safe, administrators should do a blanket update of their versions of Bash in any case.
Root Cause of this issue:
- A flaw was found in the bash functionality that evaluates specially formatted environment variables passed to it from another environment.
An attacker could use this feature to override or bypass restrictions to the environment to execute shell commands before restrictions have been applied. Certain services and applications allow remote unauthenticated attackers to provide environment variables, allowing them to exploit this issue.
- For more information about this vulnerability, refer to the following article:
Bash Code Injection Vulnerability via Specially Crafted Environment Variables (CVE-2014-6271)
Resolution for Bash Code Injection Vulnerability via Specially Crafted Environment Variables (CVE-2014-6271) (Source Redhat)
In order to avoid exploitation from CVE-2014-6271, ensure that your system is updated to at least the following versions of Bash.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 – bash-4.2.45-5.el7_0.2
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 – bash-4.1.2-15.el6_5.1
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 – bash-3.2-33.el5.1
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 Extended Lifecycle Support – bash-3.0-27.el4.2
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.6 Long Life – bash-3.2-24.el5_6.1
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.9 Extended Update Support – bash-3.2-32.el5_9.2
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.2 Advanced Update Support – bash-4.1.2-9.el6_2.1
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.4 Extended Update Support – bash-4.1.2-15.el6_4.1
- SJIS for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 – bash-4.1.2-15.el6_5.1.sjis.1
- SJIS for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 – bash-3.2-33.el5_11.1.sjis.1
- In order to update to the most recent version of the Bash package run the following command:
# yum update bash
- Specify the package name in order to update to a particular version of Bash. For example, to update a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.5 system run:
# yum update bash-4.1.2-15.el6_5.1
- The only way to fix it is to install updated Bash packages.
- The safest & simplest thing to do is to perform a system reboot.
- Carry out the following operation if system cannot be reboot.
/sbin/ldconfig
Read more information on this @ redhat